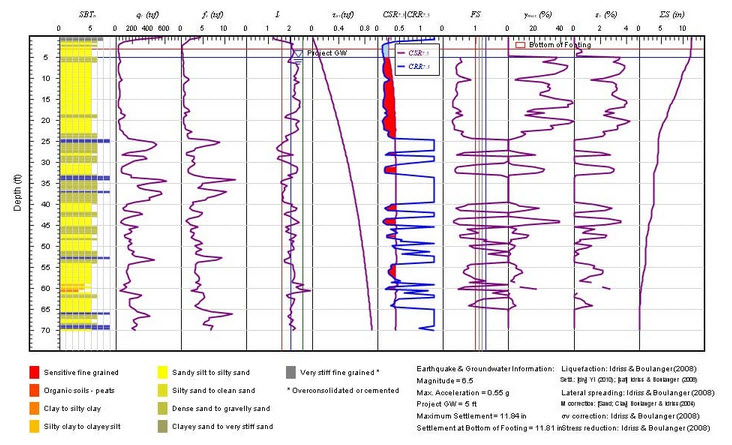
Sample CPT Test Result
The soil classification, ie. division into categories and subcategories with pertaining symbols enables understanding
of mechanical behavior of soil under the influence of load.
Traditionally, soils were divided according to grain size into noncoherent or coarse-grained soils (gravel and sand), and
coherent or fine-grained soils (silt and clay). Non-coherent soils are then categorized based on their relative proportion
in the total mass of the soil tested, while coherent soils are categorized according to their plasticity properties. The
procedure for describing and labeling of soils is called soil classification.
The world’s most widely known and used soil classification is the Unihed Soil Classification System (USCS), created
through modification ofthe Airfield Classification System (ACS). Classifications according to the British Soil
classification System (BSCS) and the Deutsches Institut fur Normung (DIN) are widely used in Europe [6]. Kovacevic
and Juric-Kacunic developed the European Soil Classification System (ESCS) for engineering purposes, which makes
use of the soil description and symbols in line with the European standard EN ISO 14688-I.
The system is based on soil classification principles prescribed in EN ISO 14688-2. In order to ensure compliance with
the European guidelines for soil description and classification, Kovacevic et al, placed emphasis on the need to
develop information support for the implementation of ESCS and USCS in order to facilitate their parallel use, ie. on
the need to transfer to and adopt the soil classification that is in line with European guidelines.
The soil classification, ie. division into categories and subcategories with pertaining symbols enables understanding
of mechanical behavior of soil under the influence of load.
Traditionally, soils were divided according to grain size into noncoherent or coarse-grained soils (gravel and sand), and
coherent or fine-grained soils (silt and clay). Non-coherent soils are then categorized based on their relative proportion
in the total mass of the soil tested, while coherent soils are categorized according to their plasticity properties. The
procedure for describing and labeling of soils is called soil classification.
The world’s most widely known and used soil classification is the Unihed Soil Classification System (USCS), created
through modification ofthe Airfield Classification System (ACS). Classifications according to the British Soil
classification System (BSCS) and the Deutsches Institut fur Normung (DIN) are widely used in Europe [6]. Kovacevic
and Juric-Kacunic developed the European Soil Classification System (ESCS) for engineering purposes, which makes
use of the soil description and symbols in line with the European standard EN ISO 14688-I.
The system is based on soil classification principles prescribed in EN ISO 14688-2. In order to ensure compliance with
the European guidelines for soil description and classification, Kovacevic et al, placed emphasis on the need to
develop information support for the implementation of ESCS and USCS in order to facilitate their parallel use, ie. on
the need to transfer to and adopt the soil classification that is in line with European guidelines.
