Earthquake Tips
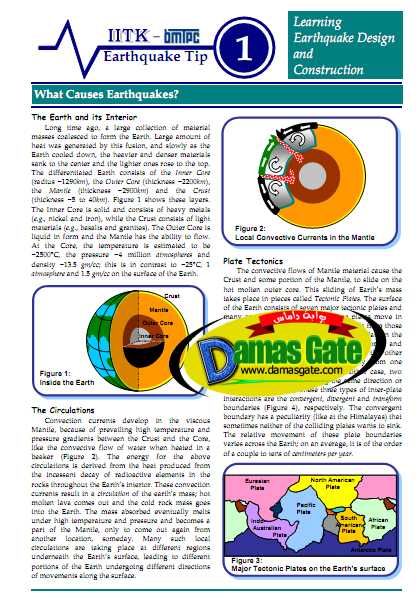
Plate Tectonics
The convective flows of Mantle material cause the Crust and some portion of the Mantle, to slide on the hot molten outer core. This sliding of Earth’s mass takes place in pieces called Tectonic Plates
. The surface of the Earth consists of seven major tectonic plates and many smaller ones (Figure 3). These plates move in different directions and at different speeds from those of the neighbouring ones. Sometimes, the plate in the front is slower; then, the plate behind it comes and collides (and mountains are formed). On the other hand, sometimes two plates move away from one another (and rifts
are created). In another case, two plates move side-by-side, along the same direction or in opposite directions. These three types of inter-plate interactions are the convergent
, divergent and transform
boundaries (Figure 4), respectively. The convergent boundary has a peculiarity (like at the Himalayas) that sometimes neither of the colliding plates wants to sink. The relative movement of these plate boundaries varies across the Earth; on an average, it is of the order of a couple to tens of centimeters per year.
Download
http://s18.alxa.net/s18/srvs2/02/001...quake.Tips.rar